list of manual therapy techniques
Manual therapy techniques are hands-on methods used to improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance functional movement. They include joint mobilization, soft-tissue work, manipulation, and fascial release, addressing musculoskeletal issues effectively.
Definition and Purpose of Manual Therapy
Manual therapy is a hands-on treatment approach aimed at improving mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing functional movement. It involves skilled techniques applied to joints, soft tissues, and fascia to address musculoskeletal disorders. The primary purpose is to restore normal joint movement, alleviate muscle tension, and promote optimal physical function. Manual therapy techniques are designed to target specific anatomical structures, ensuring precise and effective treatment. They are widely used in rehabilitation, sports medicine, and chronic pain management to enhance recovery, improve range of motion, and reduce inflammation. This approach emphasizes personalized care, tailoring interventions to meet individual patient needs.
Overview of Common Techniques
Manual therapy encompasses a variety of techniques designed to address musculoskeletal dysfunction. Common methods include joint mobilization, soft-tissue mobilization, joint manipulation, myofascial release, strain-counterstrain, and muscle energy techniques. These approaches target specific tissues and joints to restore mobility, reduce pain, and improve function. Joint mobilization focuses on passive movements to enhance joint range, while soft-tissue techniques aim to relax muscles and reduce inflammation. Manipulation involves high-velocity thrusts for immediate joint mobilization. Myofascial release targets fascial restrictions, and strain-counterstrain alleviates muscle spasms. These techniques are often combined to tailor treatment to individual patient needs, ensuring comprehensive care for optimal recovery and functional improvement.

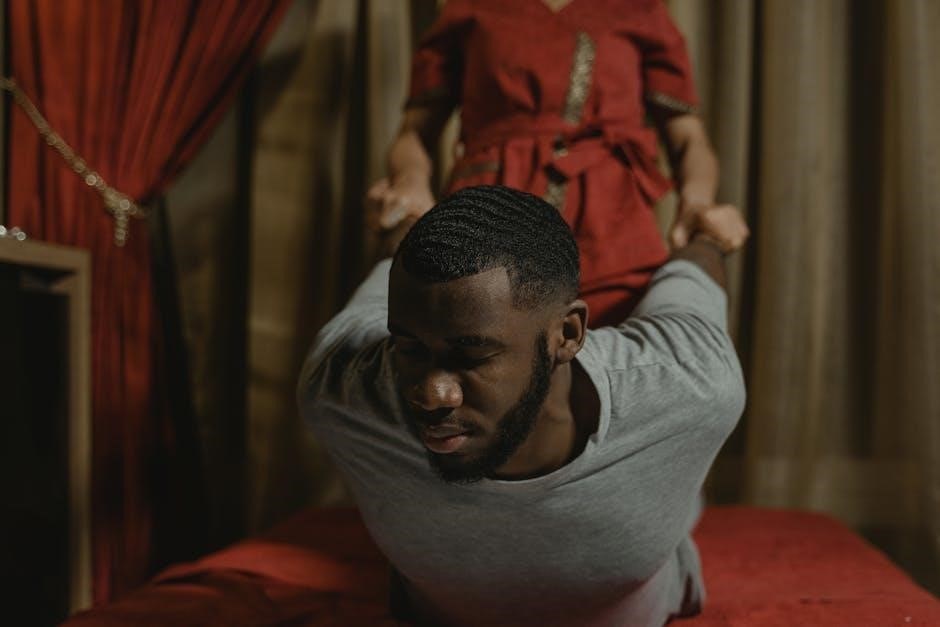
Joint Mobilization
Joint mobilization involves skilled passive movements applied to joint complexes to enhance mobility and reduce stiffness. Techniques vary in speed and range, targeting specific joint structures.
Definition and Scope of Joint Mobilization
Joint mobilization is a manual therapy technique involving a continuum of skilled passive movements applied to joint complexes. It aims to restore pain-free, functional movements by achieving full range of motion at the joint. Techniques vary in speed and range, targeting specific joint structures to address stiffness or restricted mobility. Joint mobilization is commonly used in physical therapy to provide short-term pain relief and improve joint mechanics. It is applied to synovial and cartilaginous joints, utilizing methods like distraction, gliding, or oscillations. The approach requires precision and skill to ensure safe and effective application, tailored to the patient’s specific needs and joint condition.
Benefits and Applications in Pain Relief
Joint mobilization offers significant benefits in pain relief by improving joint mobility and reducing stiffness. It is particularly effective for chronic conditions, acute injuries, and post-surgical rehabilitation. The technique enhances blood flow, breaks down adhesions, and relaxes surrounding muscles, leading to reduced inflammation and discomfort. Joint mobilization is widely used to address conditions like arthritis, tendinitis, and spinal dysfunction. Its gentle, non-invasive nature makes it suitable for patients with acute pain or limited mobility. Regular application can restore functional movements, enabling individuals to perform daily activities with greater ease and comfort, making it a cornerstone in pain management and rehabilitation strategies.
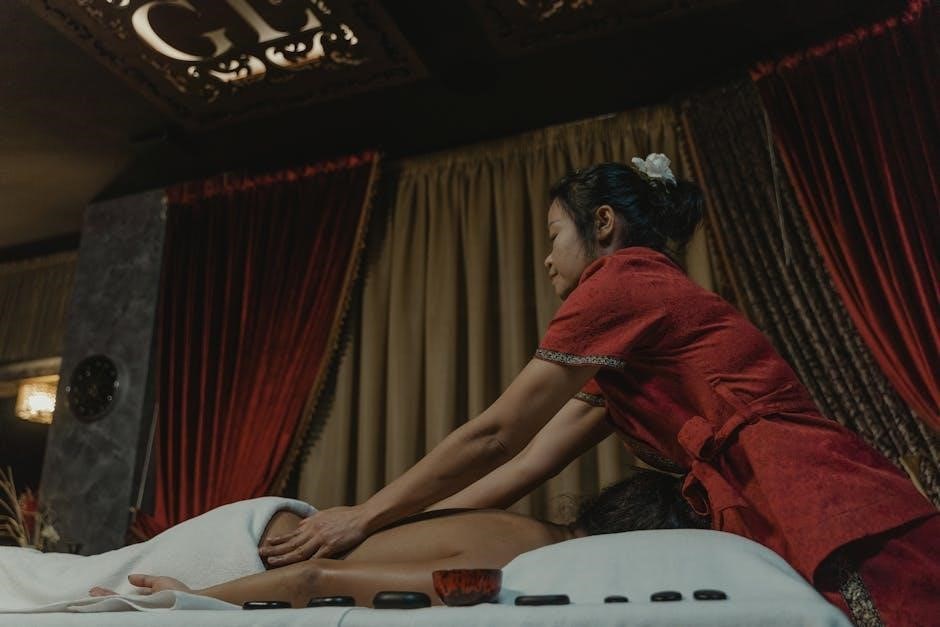
Soft-Tissue Mobilization
Soft-tissue mobilization combines pressure and stretching to relax rigid muscles, release tension, and improve fluid movement, effectively reducing pain and inflammation in targeted areas.
Techniques and Goals of Soft-Tissue Work
Soft-tissue mobilization employs targeted techniques like pressure, stretching, and breaking up adhesions to restore normal tissue function. The primary goals are to improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote healing by releasing restricted areas. Techniques may include deep tissue massage, myofascial release, and active or passive stretching. These methods aim to restore optimal movement and flexibility while addressing pain and inflammation. By addressing scar tissue and muscle imbalances, soft-tissue work enhances overall musculoskeletal function, supporting recovery and improving range of motion in both acute and chronic conditions.
Impact on Muscle Tension and Inflammation
Soft-tissue mobilization significantly reduces muscle tension by targeting tight or restricted areas, promoting relaxation and improving circulation. This technique also addresses inflammation by enhancing lymphatic drainage, which helps remove inflammatory byproducts. By breaking adhesions and scar tissue, it restores normal tissue mobility, reducing pain and stiffness. Regular application of soft-tissue work can lead to sustained decreases in muscle spasms and chronic inflammation, fostering a healing environment and improving overall musculoskeletal function. These effects make it an essential component of rehabilitation and pain management strategies.

Joint Manipulation

Joint manipulation focuses on individual joints and functional movements, employing specific techniques to improve mobility, reduce stiffness, and restore optimal joint function for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
Focus on Individual Joints and Functional Movements
Joint manipulation targets specific joints to enhance mobility and reduce stiffness. Techniques like high-velocity thrusts improve joint movement, while therapeutic stretching addresses limited range of motion. This approach restores functional movements, ensuring joints operate seamlessly during daily activities and sports. By focusing on individual joints, therapists can pinpoint and correct mechanical issues, fostering optimal alignment and reducing strain on surrounding tissues. This method is particularly effective in rehabilitation, helping patients regain lost motion and strength, thus improving overall joint function and reducing pain.
Therapeutic Stretching for Mobility
Therapeutic stretching is a key component of manual therapy, designed to enhance flexibility and improve range of motion. By targeting specific muscle groups and connective tissues, this technique helps reduce stiffness and alleviate restrictions. It is particularly effective for individuals with limited mobility due to injury or chronic conditions. Stretching promotes blood flow, relaxes tight muscles, and supports the restoration of functional movements. Regular therapeutic stretching can also prevent future injuries and improve overall physical performance, making it an essential tool in both rehabilitation and maintenance programs.

Myofascial Release
Myofascial release is a manual therapy technique targeting fascial tension to restore mobility. Gentle, sustained pressure releases fascial restrictions, improving movement and reducing chronic pain.
Techniques to Relax Fascial Tissue
Myofascial release employs gentle, sustained pressure to release fascial tension, promoting relaxation and improved mobility. Techniques include soft-tissue stretching, deep pressure, and fascial glide. Practitioners use hands-on methods to identify restricted areas, applying slow, deliberate movements to unwind tight fascia. Tools like foam rollers or therapy balls may assist in self-release, while manual approaches focus on precise targeting. The goal is to restore fascial elasticity, reducing stiffness and enhancing fluid movement. These methods are often combined with breathing exercises to further release tension and improve overall fascial health.
Applications in Chronic Pain and Limited Mobility
Myofascial release is widely used to address chronic pain and mobility limitations by targeting fascial restrictions. Techniques such as soft-tissue mobilization and joint mobilization help reduce stiffness and improve range of motion. In cases of chronic pain, these methods alleviate tension in connective tissue, promoting relaxation and reducing discomfort. For individuals with limited mobility, manual therapy enhances flexibility and restores functional movement. These approaches are particularly effective in managing conditions like fibromyalgia and chronic musculoskeletal pain, offering a non-invasive solution to improve quality of life and physical function.
Strain-Counterstrain Technique
Strain-counterstrain technique involves gentle, sustained pressures to relieve muscular spasm and pain by targeting specific tender points and joint restrictions, enhancing relaxation and mobility.
Principles and Methods of Strain-Counterstrain
Strain-counterstrain technique employs gentle, passive holding of joints and soft tissues in specific positions to reduce muscle spasms and pain. Practitioners identify tender points and apply sustained, non-painful pressures to relieve tension. This method focuses on addressing restricted joints and muscles by encouraging relaxation and restoring normal movement patterns. The approach avoids forceful manipulations, emphasizing comfort and patient tolerance. By targeting the underlying causes of dysfunction, strain-counterstrain promotes improved joint mobility and reduces discomfort, making it an effective tool in pain management and rehabilitation.
Efficacy in Reducing Muscular Spasm
Strain-counterstrain is highly effective in reducing muscular spasms by targeting specific tender points. The technique involves gentle, sustained pressures that alleviate tension without causing pain. By addressing restricted joints and muscles, it promotes relaxation and restores normal movement. Clinical studies show significant reductions in muscle spasms and pain levels. Its non-invasive nature makes it ideal for sensitive patients. This method is widely used in rehabilitation settings to enhance mobility and comfort. The approach focuses on restoring balance to the musculoskeletal system, offering long-term relief from spasms and associated discomfort;
Muscle Energy Techniques
Muscle energy techniques enhance joint mobility and strength by engaging patient-controlled isometric contractions, improving neuromuscular coordination and reducing stiffness.
Approach to Improving Joint Mobility
Muscle energy techniques (METs) involve patient-controlled isometric contractions to improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. The therapist guides the patient to engage specific muscles, applying gentle resistance to enhance neuromuscular coordination. This approach targets joint dysfunction by breaking adhesions, improving synovial fluid circulation, and restoring normal movement patterns. By focusing on voluntary muscle activation, METs empower patients to actively participate in their recovery, promoting strength and flexibility. This method is particularly effective for addressing restrictions in range of motion while minimizing discomfort, making it a valuable tool in both rehabilitation and sports therapy settings.
Role in Enhancing Muscular Strength
Muscle energy techniques (METs) actively engage patients in strengthening exercises, leveraging controlled isometric contractions to target specific muscle groups. By applying gentle resistance, therapists help improve muscle endurance and power, fostering neuromuscular coordination. This approach enhances proprioception, allowing muscles to function more efficiently. METs are particularly effective for addressing muscle imbalances and weakness, promoting overall muscular strength without causing excessive strain. The active participation of patients makes METs a valuable tool for rehabilitation, sports performance, and chronic condition management, ensuring sustainable gains in muscular function and mobility.

Fascial Stretch Therapy
Fascial Stretch Therapy (FST) is a hands-on technique targeting the fascial system to enhance flexibility and reduce stiffness. It improves mobility and reduces pain, benefiting both rehabilitation and sports performance.
Techniques for Improved Flexibility
Fascial Stretch Therapy (FST) employs gentle, sustained stretching and oscillatory movements to target the fascial system. These techniques enhance flexibility by reducing fascial tension and improving joint mobility. Practitioners use tables or floors to apply precise stretches, focusing on entire chains of movement rather than isolated muscles. This approach not only lengthens fascial tissues but also promotes relaxation and circulation. FST is particularly effective for addressing restrictions in the lower back, hips, and shoulders. By improving range of motion, it supports rehabilitation, postural alignment, and athletic performance, making it a versatile tool in manual therapy.

Applications in Sports and Rehabilitation
Manual therapy techniques are widely applied in sports and rehabilitation to enhance recovery, improve performance, and restore function. In sports, techniques like joint mobilization and soft-tissue work reduce muscle tension, prevent injuries, and improve flexibility, enabling athletes to perform at higher levels. In rehabilitation settings, these methods aid in post-surgical recovery, address chronic pain, and restore movement after injuries. By targeting specific areas of restriction, manual therapy accelerates healing, enhances mobility, and supports long-term functional recovery, making it an essential tool for both athletes and patients undergoing rehabilitation.
